The Surveillance of Julian Assange
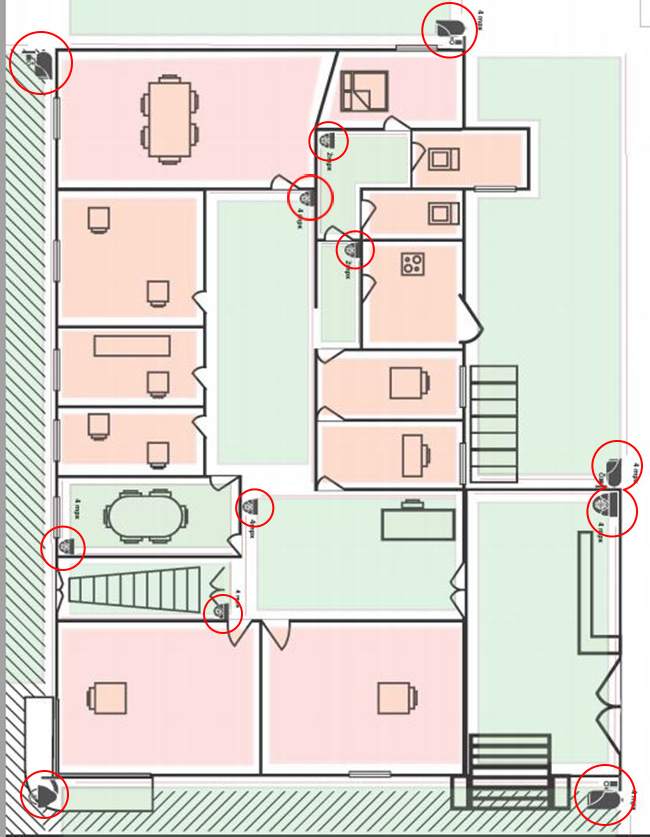
Surveillance Architecture of Julian Assange at the Ecuadorian Embassy (2012-2019)
Bottom Line up Front (BLUF)
Analysis of the sophisticated multi-layered surveillance operation targeting Julian Assange during his asylum at the Ecuadorian Embassy in London. The operation, internally designated "Operation Hotel" by Ecuador, cost over $5 million and involved state intelligence services, private security contractors, and diplomatic staff. The Ecuadorian Embassy represented an unprecedented convergence of state and private intelligence operations, constituting what intelligence sources describe as "the most surveilled place on earth"
Over 5,000 visitors systematically monitored and profiled
Constitutional violations including attorney-client privilege breaches
International intelligence collaboration spanning CIA, Spanish CNI, and Ecuadorian services
Escalation to kinetic operations planning (kidnapping/assassination plots)
Geopolitical leverage mechanisms tied to IMF loans and diplomatic normalization
I. SURVEILLANCE ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
Primary Contractor: UC Global
Owner: David Morales
Contract Value: $55,000-$97,000 monthly
Legal Status: Under Spanish prosecution for privacy violations, bribery, and money laundering
Intelligence Affiliations: Simultaneous collaboration with CIA and Spanish CNI
Audio-Visual Systems
Comprehensive Coverage:
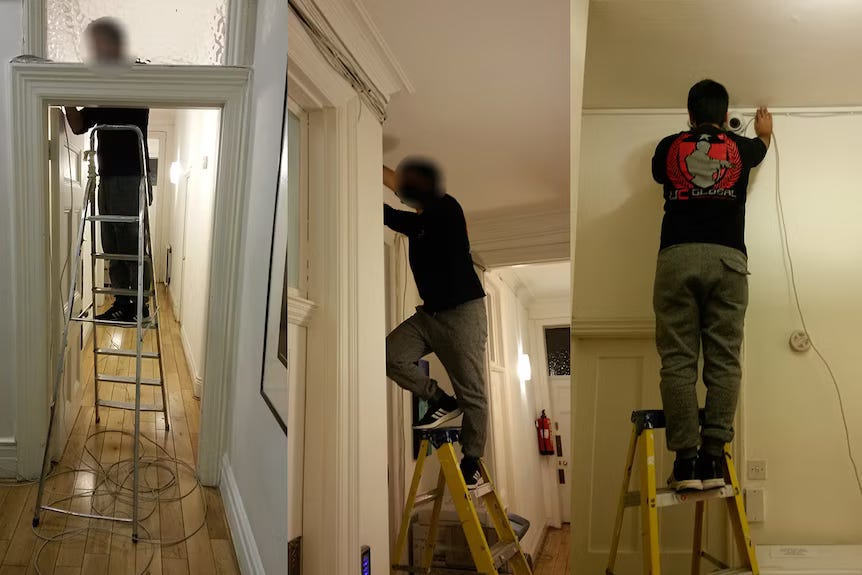
Cameras with integrated microphones installed in all common areas
Hidden microphones concealed within:
Fire extinguishers
Decorative objects
Women's bathroom (toilet removed at Assange's request for private meetings)
Audio Range: 10-meter capture radius
Real-time Capability: Live streaming accessible remotely
Technical Architecture:
Direct CIA access to live feeds and archived recordings
Video data routed through IP addresses linked to Las Vegas Sands hotels
Zohar Lahav (Las Vegas Sands security chief) served as CIA conduit
Psychological Monitoring
Behavioral Documentation:
Sleep pattern analysis
Mood fluctuation tracking
Smoking habit monitoring
Gift receipt documentation (including items thrown onto embassy balcony)
Medical condition observations
III. VISITOR INTELLIGENCE OPERATIONS
A. Systematic Profiling Program
Scale: Over 5,000 individuals catalogued Data Collection Protocol:
Passport seizure and photography
Device confiscation and technical exploitation
Nationality documentation
Visit purpose classification (medical, legal, personal)
Duration tracking
Notable Visitors:
Legal: Gareth Peirce, Baltasar Garzón
Political: Yanis Varoufakis
Celebrity: Pamela Anderson, Vivienne Westwood
Journalistic: Multiple investigative reporters
B. Technical Exploitation
Device Compromise:
Phone disassembly for IMEI cloning
Data extraction from electronic devices
Spyware installation on family devices of former President Correa
Access to chats, emails, and intimate photographs
C. DNA Intelligence Collection
Biological Surveillance Attempt:
Plot to steal infant diaper for DNA analysis
Objective: Paternity confirmation for Assange's child
Strategic Purpose: Complicate asylum protections through family rights implications




IV. DIGITAL ESPIONAGE OPERATIONS
A. Network Infiltration
Embassy Systems:
Accusations of Assange hacking diplomatic systems to access to classified diplomatic cables
Countermeasures: Sensitive files secured in physical safe
B. Cyber Arsenal Deployment
Vault 7 Response:
2010: Assange designated for "Manhunting Timeline"
Significant operational escalation following 2017 CIA cyber tools exposure
Enhanced surveillance technology deployment
Export control violations: UC Global may have illegally exported surveillance technology from Spain to UK without proper licensing
Technology sourcing from Israeli and American companies with intelligence ties
Regulatory violations raising compliance red flags
Reclassification Operations:
Internal CIA memos debated redefining WikiLeaks as "non-state hostile intelligence service"
Reclassification enabled more aggressive covert operations
Vault 7 publications served as tipping point for escalated surveillance campaign
V. INTELLIGENCE COLLABORATION
A. CIA Integration
Operational Framework:
Direct access to surveillance feeds - with data routing through Las Vegas Sands infrastructure
Zohar Lahav as operational liaison
"CIA" folder discovered on David Morales' hard drive containing visitor videos
B. Spanish Intelligence Coordination
Dual Loyalty Operations:
David Morales concurrent collaboration with Spanish CNI
Coordination with U.S. intelligence services
Complex jurisdictional and legal implications
C. Miscellaneous
UK Complicity: MI6 collaborated on exfiltration interdiction; aware of CIA surveillance.
Ecuador’s Role: actively permitted UC Global espionage; later revoked asylum (April 2019).
Russian Involvement: Attempted diplomatic extraction via Ecuadorian cover; Assange would acquired Ecuadorean nationality, be named as a diplomat, appointed to serves as the political counselor to the Ecuadorean Embassy in Moscow.
VI. Kinetic Operations Planning
Escalation Scenarios included kidnapping, rendition, and assassination options. Operational concepts progressed to advanced stages but were ultimately vetoed due to legal, diplomatic, and oversight constraints. Wikileaks disclosure of hacking capabilities (Vault 7) was considered by some “the largest data loss in CIA history.”
Operational method:
Spanish asset UC Global tasked with mapping embassy security, routines, and vulnerabilities
Covert entry into Ecuadorian Embassy by "leaving the door open" to stage an "accidental" breach
Render Assange to the U.S. or a third country. Debated in London vs. "Pakistan/Egypt" (deemed lower-risk
Sketches for lethal force requested, specifically, poison; framed as offensive counterintelligence against a hostile foreign service
VII. LEGAL AND CONSTITUTIONAL VIOLATIONS
A. Attorney-Client Privilege Breaches
Systematic Violations:
Hundreds of hours of legal consultations recorded
Compromise of U.S. extradition defense strategy
Spanish court confirmation of constitutional violations
Video evidence presented to lawyers during Spanish proceedings
B. Judicial Proceedings
Spanish Investigation:
Judge Santiago Pedraz leading investigation
Charges against David Morales: privacy violations, bribery, money laundering
Spanish High Court ruling: surveillance illegal and unrelated to embassy security
U.S. judicial assistance requests for House Intelligence Committee cooperation
C. U.S. Legal Challenges
Civil Litigation:
Lawsuit filed by Assange's associates against CIA, Mike Pompeo, UC Global, and David Morales
Allegations: Constitutional rights violations, privacy breaches, recording private conversations, copying devices
U.S. District Court Judge John Koeltl partial rejection of CIA dismissal motion
Court ruling confirmed potential breach of privacy rights if CIA accessed plaintiffs' phones
Some claims dismissed (surveillance of conversations and passport copying)
Ongoing discovery process regarding device access and surveillance scope
Congressional and Executive Accountability:
Spanish Judge Santiago Pedraz requested judicial assistance from U.S. House Intelligence Committee
Investigation targets: UC Global operations, CIA involvement, surveillance architecture
Named potential victims: former U.S. Representative Dana Rohrabacher, former Ecuadorian President Rafael Correa
Former U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo summoned by Spanish court to explain kidnapping and assassination plot allegations
U.S. Department of Justice accused by Spanish judges of obstructing UC Global investigation
Challenges in holding U.S. entities accountable for international surveillance operations
VIII. FINANCIAL AND OPERATIONAL SCALE
A. Financial Investment
Operation Hotel Costs:
Total expenditure: $5+ million
UC Global contract: $55,000-$97,000 monthly
Additional undercover agents: $35,000 monthly
24/7 surveillance operations from nearby safe house
B. Human Intelligence Resources
Operational Staffing:
Shift-based guard rotations
Undercover agent deployment of American, British and Russian agencies, among others, stationed around the Ecuadorian Embassy.
Police movement monitoring
Protest surveillance operations
C. Operational Security Measures
Internal Provocations:
UC Global employees discussed planting compromising materials (hard drives or USB sticks) to fabricate grounds for expulsion or arrest
USB drives and hard drives as fabricated evidence
Infiltration through false journalist credentials with operatives posing as visitors or journalists
Long-term watchlisting of visiting journalists in their home countries
Attempts to gather intelligence or provoke compromising behavior through infiltration
IX. MOTIVATIONS AND LEVERAGE
A. Political Pressure Mechanisms
U.S. Influence Operations:
President Moreno's use of Assange as bargaining chip for geopolitical realignment and diplomatic normalization with Ecuador
Leverage for IMF loan negotiations
Trade deal facilitation
INAPapers Scandal:
Leaked internal communications revealed Ecuador's government simultaneously condemned Assange publicly while covertly leaking data about him to U.S. entities
Evidence of orchestrated public-private collaboration between Ecuador and U.S. intelligence
Dual-track diplomatic strategy: public condemnation, private cooperation
Extortion and Criminal Activity:
2019: Private recordings including medical reports surfaced in Spain
Criminals demanded €3 million ransom to prevent leak of surveillance materials
X. KEY PERSONNEL AND ENTITIES
Primary Actors
David Morales: UC Global owner, Spanish prosecution subject
Zohar Lahav: Las Vegas Sands security chief, CIA liaison
Lenín Moreno: Ecuadorian President (2017-2021), operation escalation
Mike Pompeo: Former U.S. Secretary of State, Spanish court summons
Judge Santiago Pedraz: Spanish investigating magistrate
Legal Representatives
Baltasar Garzón: Assange's lawyer, surveillance victim
Gareth Peirce: Legal counsel, monitored meetings
Stella Morris: Assange's partner, surveillance target
Intelligence Entities
CIA: Primary U.S. intelligence beneficiary
NSA: Manhunting Timeline designation
Spanish CNI: Collaborative intelligence partner
UC Global: Primary surveillance contractor
Broader Operational Context
Circumstances leading to asylum request included Swedish extradition warrant context given fabricated sexual assault allegations in Sweden (Anna Ardin and Sofia Wilén cases) – later dropped in 2017. The full extent of Media Management and Narrative Control related to Wikileaks is beyond the scope of this brief. UK Supreme Court ruling on extradition lead to tactical decision to begin diplomatic negotiations between Ecuador, UK, and Sweden given International legal framework regarding diplomatic asylum. Manning cases superseding indictments and led to charge expansion. Medical assessments during embassy confinement showed general health decline, Vitamin D deficiency and psychological effects of isolation. In addition to these measures, attempts where actively being made to strangle Wikileaks financial infrastructure through payment processor boycotts (Visa, MasterCard, PayPal), asset freezes, bankings restrictions, account closures and other forms of financial pressure – thereby attempting to cut off Assange’s resources (primarily donations) for legal costs. These included hacking digital infrastructure, intercepting and disrupting encrypted communications, provoking internal disputes within the organization, planting damaging information, and physically stealing electronic devices and wiping hard drives, as well as includes targeting known associates, friends, journalists, supporters, lawyers, and family members. Ecuador's newly elected government revoked the status in April 11, 2019 due to President Moreno's diplomatic calculations. Leading to Metropolitan Police arrest operation inside embassy and transfer to Belmarsh Prison pending U.S. extradition on sealed indictment under the Espionage Act and Computer Fraud and Abuse Act.
XI. CONCLUSION
The surveillance operation against Julian Assange represents a paradigmatic shift in intelligence operations, characterized by the convergence of state and private actors, the systematic violation of constitutional protections, and the weaponization of diplomatic processes. The operation's scope, intensity, and legal impunity established operational precedents for future intelligence activities against journalists, publishers, and dissidents.
The designation of the Ecuadorian Embassy as "the most surveilled place on earth" reflects not merely the technical sophistication of the surveillance apparatus, but the fundamental transformation of intelligence operations in the digital age. This case study demonstrates how diplomatic asylum can be systematically undermined through collaborative intelligence operations, and how constitutional protections can be circumvented through jurisdictional manipulation and private contractor utilizations.
The ongoing legal proceedings in Spain and the United States will likely determine the extent to which such operations can be conducted with impunity, and whether international law provides meaningful protection for journalists and publishers operating in the contemporary intelligence environment.