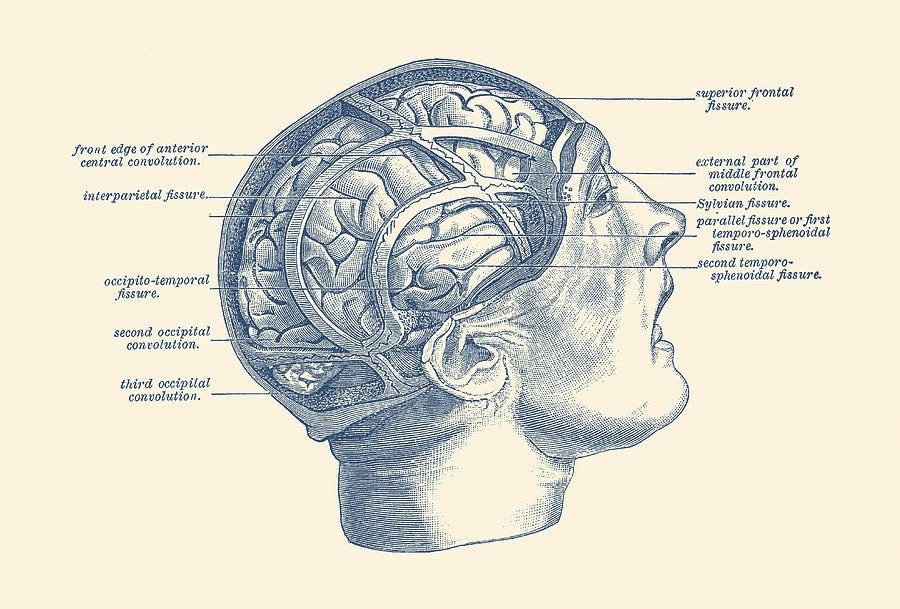
Bottom Line Up Front (BLUF)
This comprehensive intelligence assessment examines pharmacological interrogation research and operational deployment spanning 78 years across 12+ nations and security services. The analysis reveals a systematic evolution from experimental programs to contemporary operational capabilities, with significant sophistication in compound selection and delivery methods. Key Findings
Pharmacological interrogation represents a globally entrenched intelligence capability, operationalized by ≥12 states since 1922. While no compound reliably extracts "ground truth" under all conditions—a limitation shared by all elicitation techniques—47+ agents across 7 drug classes are systematically deployed for compliance induction, memory impairment, and behavioral subjugation. These compounds are designed to induce speech rather than ensure truthfulness.
Evolution of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs): Deployment has progressed from crude interrogation adjuvants (1920s) through state-sponsored mass testing programs (1947–1973) to contemporary medically obscured tactics including off-label dosing, aerosol delivery, and withdrawal exploitation. Deniable medical cover and euphemisms like “safety officers” has become standard operational practice.
Institutional obfuscation: The destruction of 90% of MKULTRA records (1973) and deliberately narrow investigatory mandates (e.g., GTMO Inspector General investigations) systematically conceal operational scale. Contemporary programs remain highly classified, weaponizing plausibly deniable medical use cases for operational cover.
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
Origins and Early Research (1922-1945)
The documented history of pharmacological interrogation begins in 1922 with Dr. Robert House's scopolamine experiments at Dallas County jail, inducing "twilight sleep" states in subjects. By the 1930s, Northwestern University's Scientific Crime Detection Laboratory had institutionalized these methods.
Nazi German Research (1940-1945): Extensive experimentation at Dachau concentration camp tested barbiturates, morphine derivatives, mescaline, and scopolamine to "eliminate prisoner will," as documented in autopsy reports and Nuremberg Trial evidence.
U.S. Intelligence Programs (1942-1973)
OSS Initiation (1942): General William "Wild Bill" Donovan authorized the first documented American intelligence program to modify human behavior through chemical means, studying barbiturates, caffeine, peyote, scopolamine, cannabis, and alcohol. Notably, they determined that the best "TD" (Truth Drug) was a potent cannabis extract followed by caffeine and alcohol for lowering inhibitions in "recalcitrant interrogation subjects"
Operation PAPERCLIP Integration: German research directly influenced subsequent U.S. programs (CHATTER, BLUEBIRD, ARTICHOKE) through the recruitment of Nazi scientists including Dr. Hubertus Strughold.
MK-Program Expansion (1951-1973): Beginning with QKHILLTOP (1951-1953), the Office of Technical Services developed multiple programs including MK-ULTRA, MK-SEARCH, MK-OFTEN, MK-CHICKWIT, MK-DELTA, and MK-NAOMI. These studies tested 26,000+ compounds on:
Prisoners (Holmesburg Prison)
Military personnel (Edgewood Arsenal)
Psychiatric patients (Canadian Allan Memorial Institute)
Civilians (San Francisco and New York City brothels)
POWs (post-war detention centers in Atsugi, Kanagawa)
This represents the largest documented toxicity and human behavioral testing program in recorded history.
Narcohypnosis Development: Advanced techniques combined barbiturate sedation with stimulant administration to maintain subjects in a "twilight zone" optimal for interrogation. CIA protocols used simultaneous IV drips—one depressant, one stimulant—allowing real-time adjustment of consciousness levels. Specific drug combinations included:
Seconal (barbiturate) + Dexedrine (amphetamine)
Pentothal (barbiturate) + Desoxyn (methamphetamine)
Occasional marijuana ("sugar")
Supporting agents: Thiamine, Sodium luminal, Atropine sulfate, Sodium pentothal, Caffeine sulfate
Research determined that 2-3 drugs worked optimally; more than that led to complications and unpredictability.
Institutional Destruction and Obfuscation
The systematic destruction of historical documentation combined with ongoing classification of current programs indicates this assessment represents only the visible aspects of potentially much larger operational capabilities. The absence of publicly available controlled experimental studies necessitates reliance on incomplete psychiatric evidence and anecdotal law enforcement reports.
MK-File Destruction (1973): CIA Director Richard Helms ordered the destruction of an estimated 90% of original MK program documentation, leaving 94 sub-projects without identifiable titles or purposes. The subsequent release of sensational LSD experimentation served as a limited hangout, given LSD's operational inefficacy.
Investigatory Limitations: DoD Inspector General investigations were deliberately constrained to examine only "mind-altering drugs to facilitate interrogations," intentionally excluding drugs administered under medical pretexts.
CONTEMPORARY OPERATIONAL DEPLOYMENT (2001-2025)
Legal Precedent and Judicial Approval
Aurora Case (2012): Court-approved narcoanalysis for James Holmes established judicial precedent for court-sanctioned chemical interrogation in the United States.
Current Operational Methods
Contemporary deployment demonstrates significant evolution in sophistication:
Delivery Mechanisms:
Crude injection/oral administration (1947-1973)
Aerosolized delivery and environmental contamination (1980s-2000s)
Medical cover exploitation (2001-2025)
Faulty diagnoses (schizophrenia, anxiety, motion sickness)
Withdrawal exploitation
Combinatorial effects manipulation
Off-label dosing (e.g., high-dose scopolamine for "motion sickness")

PHARMACOLOGICAL TAXONOMY
I. ANLINERGICS
Mechanism: Acetylcholine blockade → delirium, amnesia, suggestibility
Scopolamine (Hyoscine)
1922: Dallas County jail "twilight sleep" experiments (Dr. Robert House)
1930s: Northwestern University Scientific Crime Detection Laboratory standardization
1943: Nazi Dachau experiments for "prisoner will elimination" (documented in autopsy reports)
1947-1953: U.S. Navy Project CHATTER interrogation studies (alongside mescaline, anabasine, LSD-25)
Korean War: "Repressed memory" recovery and soldier malingering detection protocols
1950s-1970s: KGB SP-117 operational deployment in Eastern Bloc operations
2009: Czechoslovak secret police confession extraction from anti-state dissidents (proven documentation)
Guantánamo SOP: Transdermal patches administered to all detainees rendered to Cuban facility (declassified medical SOP)
2015-2025: Colombian cartel aerosolized deployment inducing "zombie compliance" (>50,000 robberies, U.S. Overseas Security Advisory Council bulletins)
3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate (BZ)
1968: U.S. Army Vietnam munitions dispersal causing 72-hour delirium (Project DORK)
1995: Russian FSB Chechen hostage crisis deployment (confirmed via Moscow hospital toxicology screens)
II. BARBITURATES
Mechanism: GABAergic CNS depression → disinhibition
Sodium Amytal (Amobarbital)
1930: Dr. William Bleckwenn catatonic patient "lucid intervals" (published JAMA studies)
1943: OSS POW interrogations yielding contradictory intelligence (declassified OSS Field Manual No. 6)
2008: Ajmal Kasab post-Mumbai attacks administration (India Central Bureau of Investigation affidavits)
2012: James Holmes court-approved narcoanalysis for insanity plea (Aurora Case legal precedent)
Sodium Thiopental
1957-1964: Dr. Cameron's Allan Memorial Institute "depatterning" experiments (Canadian Senate Subcommittee testimony)
2007: India Noida serial killer confession extraction (Delhi High Court evidence logs)
III. BENZODIAZEPINES
Mechanism: GABA enhancement → anterograde amnesia
Midazolam
2001-2006: CIA rendition "capture packages" intramuscular administration (documented in Abu Zubaydah flight manifests)
2013: South Africa Mangaung Prison forced injections (Legal Resources Centre video evidence)
Flunitrazepam
2010: Israeli Shin Bet Palestinian detainee protocols (documented in B'Tselem prisoner testimonies)
Withdrawal Exploitation: Intentional cessation triggering seizures for confession extraction
IV. HALLUCINOGENS
Mechanism: Serotonin agonism → altered perception
LSD
1953: CIA Operation Midnight Climax brothel experiments (Senate Church Committee Hearings Vol. I)
1962: UK Porton Down servicemen trials (2006 UK Ministry of Defence compensation records)
Mescaline
1944: Nazi Dachau truth serum trials (Nuremberg Trials Document NO-085)
1951: U.S. Project CHATTER naval tests (CIA Technical Report TR-3)
Ketamine
2003: Macedonia Abu Omar abduction and rendition (European Court of Human Rights ruling El-Masri v. Macedonia)
V. STIMULANTS
Mechanism: Dopamine/norepinephrine release → agitation
Amphetamines
1942: OSS ethanol combination interrogations (OSS Morale Operations Division files)
2004: Iraq Camp Nama covert food contamination (Taguba Report Annex 26)
Modafinil
2005: Guantánamo sleep deprivation protocols (Physicians for Human Rights audit)
VI. ANTIPSYCHOTICS
Mechanism: Dopamine blockade → chemical restraint
Haloperidol
2002-2008: Guantánamo "Behavioral Pacification" of Mohamedou Salahi (documented in camp medical logs)
Forced injection protocols for non-compliant detainees
2019: Iran Aminabad Hospital political prisoner injections (UN Special Rapporteur report E/CN.4/2005/7)
Chlorpromazine
2003: Guantánamo Mohammed al-Qahtani hypersedation regimen (DoD interrogation memos)
Metabolic disruption and hypersedation effects
Quetiapine
Maintenance dosing for affect flattening and resistance reduction
VII. MISCELLANEOUS AGENTS
Mefloquine
2002-2009: Guantánamo neuropsychiatric weaponization (FDA adverse event database documentation)
Prophylactic administration at 500% FDA limits despite negligible malaria risk at Cuban facility
Curare/Tubocurarine
1976: Uruguay paralysis during interrogations (OAS Inter-American Commission files)
Anxiolytics
Diazepam oral administration for transport compliance (plausibly deniable medical purpose)


ASSESSMENT AND IMPLICATIONS
Operational Effectiveness
While no pharmacological agent reliably extracts ground truth under all conditions—a limitation inherent to all elicitation techniques—these compounds serve distinct tactical purposes:
Compliance Induction: Reducing physical and psychological resistance
Memory Impairment: Preventing accurate recollection of interrogation procedures
Behavioral Subjugation: Establishing interrogator control over subject responses
Speech Induction: Increasing verbal output without guaranteeing truthfulness
Contemporary Focus Shift
Current operational emphasis has shifted from experimental research to deployment of proven compounds, with sophisticated attention to:
Medical cover and legal deniability
Refined delivery mechanisms
Exploitation of legitimate medical procedures
Integration with psychological interrogation techniques


CONCLUSION
Pharmacological interrogation represents one of the longest-running and most systematically developed intelligence programs in recorded history. The evolution from crude experimental phases to sophisticated operational deployment demonstrates sustained institutional commitment across multiple nations and decades.
The 47 documented agents across 7 pharmacological categories confirm that chemical interrogation methods remain globally entrenched in standard intelligence practice. Contemporary programs appear to prioritize operational deployment over research, emphasizing medical cover and legal deniability to maintain program security and political viability.
The systematic obfuscation of program scope through document destruction and classification suggests the true extent of these capabilities remains largely concealed from public scrutiny, indicating ongoing operational significance within the global intelligence community.
End of Brief